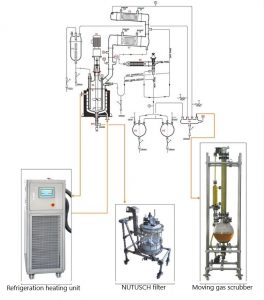
Working Principle of Glycol Chiller
For the low-temperature chiller using ethylene glycol solution, we
call it glycol chiller. Its outlet water temperature is generally below – 10 ℃, and the specific temperature requirements shall be subject to the
needs of users. Glycol chillers are common in chemical plants. In order to
ensure the safe and stable operation of equipment, many chemical plants will
strictly require water chillers to take explosion-proof measures, that is, what
we often call explosion-proof water chillers.
The structural composition of the water chiller is roughly the same,
which is composed of compressor, evaporator, condenser, throttling element and
electric control system. However, the glycol chiller adopts low-temperature
compressor and is equipped with economic separator and other components, which
are still different.
1、In order to keep the
pressure in the evaporator low enough to ensure that the refrigerant evaporates
at a sufficiently low boiling temperature, a compressor is used to extract the
evaporated refrigerant gas, that is, the refrigerant steam with low temperature
and low pressure is compressed into a refrigerant gas with high temperature and
high pressure. When the suction speed of the compressor is greater than the
evaporation speed of the refrigerant, the evaporation pressure and evaporation
temperature will decrease. Conversely, the suction speed of the compressor is
less than that of the refrigerant, and the evaporation temperature and pressure
will rise accordingly.
2、 High temperature and
high pressure refrigerant is condensed into liquid in the condenser. In the
condenser, the refrigerant releases heat to air or water lower than its
temperature. This part of heat includes the heat absorbed when the refrigerant
evaporates in the evaporator and the heat converted when the compressor
compresses. Special attention: the temperature of air or water must be lower
than that of refrigerant, otherwise the refrigerant cannot release heat, that
is, the temperature of cooling medium (cooling tower water or air) must be lower
than that of refrigerant gas at the outlet of compressor.
3、Through the restrictor,
the pressure of the refrigerant drops from the condensation pressure to the
evaporation pressure. The liquid from the condenser is stored in the liquid
reservoir. At this time, the refrigerant is in the state of normal temperature
and high pressure. After passing through the expansion valve, the boiling point
decreases due to the decrease of pressure. After entering the evaporator, the
liquid is easy to absorb heat and evaporate.
Recomendaciones relacionadas
-
The Phenomenon of Ice Jam in Low Temperature Chiller System
1336The phenomenon of ice jam in low temperature chiller system is mainly due to the excessive water in the refrigeration system. With the continuous circulation of refrigerants, the water in the refrigeration system gradually concentrates at the outl...
Ver detalles -
The difference between air-cooled and water-cooled 15P refrigeration units
2003Because the demand conditions are different, when the selected 15P refrigeration unit is air-cooled and water-cooled, what is the difference? The air-cooled 15P refrigeration unit contains a heat-insulating water tank and water pump in its body, w...
Ver detalles -
Why do electrical companies need cooling system industrial chillers?
1803When electrical equipment is operating outdoors, it may encounter high temperature environments. For example, in direct sunlight in the summer, the temperature may be very high. If the equipment overheats, it will affect performance or even ...
Ver detalles -
¿Por qué hay aire en el sistema de control de temperatura del reactor?
1570El gas de impurezas en el sistema de control de temperatura del reactor es para aumentar la presión de condensación del sistema de refrigeración, aumentando así la temperatura de condensación, el aumento de la temperatura de escape del compresor, el aumento de la poten...
Ver detalles
 LNEYA Enfriadoras industriales Fabricante Proveedor
LNEYA Enfriadoras industriales Fabricante Proveedor